Did you know that the human body has different types of fat?
When most people think about body fat, they’re usually picturing subcutaneous fat—the fat that resides just beneath the skin. This type of fat is commonly found on areas like the abdomen, thighs, and upper arms. In this article, we’ll delve deeper into subcutaneous fat: what it is, where it comes from, and how you can manage it.
Types of Fat in the Body
To begin, let’s understand the different types of fat in the body. Fat, or adipose tissue, serves essential functions such as storing energy, protecting organs, and insulating the body. There are three primary types of adipose tissue:
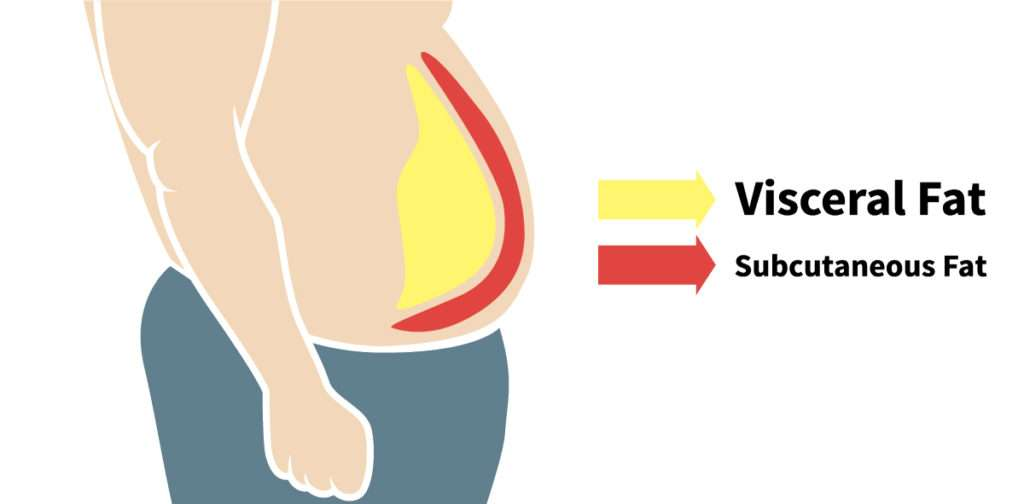
1. Visceral Fat: Found deep within the abdominal cavity, surrounding internal organs.
2. Intramuscular Fat: Located within skeletal muscles.
3. Subcutaneous Fat: Found just beneath the skin, covering most of the body.
Each type of fat plays a role in maintaining bodily functions. However, having excessive amounts of fat, particularly visceral or subcutaneous fat, can lead to negative health outcomes.
What is Subcutaneous Fat?
Subcutaneous fat is the most visible type of fat, located directly under the skin. While it’s natural and necessary to have some subcutaneous fat, excessive amounts can pose health risks. Factors like genetics, diet, and lifestyle largely determine how much subcutaneous fat a person has.
Unlike visceral fat, which surrounds internal organs and is linked to severe health conditions, subcutaneous fat serves as an energy reserve and helps cushion the body. However, when present in excess, it can still lead to health issues such as insulin resistance, inflammation, and cardiovascular problems.
What Causes Subcutaneous Fat?
Subcutaneous fat is a normal part of the human body, but several factors can contribute to an unhealthy accumulation:
1. Lifestyle Habits: Diet and activity levels are significant contributors. Consuming more calories than you burn regularly leads to fat storage, including subcutaneous fat. Diets high in refined sugars, processed foods, and unhealthy fats are particularly linked to weight gain. A sedentary lifestyle further exacerbates fat accumulation.
2. Medical Conditions: Certain conditions, such as hypothyroidism or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can make it harder for the body to regulate fat storage. Hormonal imbalances can also lead to increased fat accumulation, even in individuals who maintain an active lifestyle.
How to Measure Subcutaneous Fat
Understanding how much subcutaneous fat your body has is a crucial step toward managing your health. Here are some methods to measure it:
1. Body Composition Scales: These are commonly available and provide estimates of overall body fat percentage, though they may not isolate subcutaneous fat precisely.
2. Calipers: Skinfold measurements using calipers offer a simple and inexpensive way to estimate subcutaneous fat levels. While not as accurate as advanced methods, it’s a practical option for personal use.
3. Ultrasonography: This method uses sound waves to measure fat thickness under the skin. It’s a safe, affordable, and non-invasive way to track changes in fat levels over time.
4. CT Scans and MRIs: These advanced imaging methods provide highly accurate measurements of subcutaneous and visceral fat. However, they’re expensive and not practical for regular use.
Understanding your body composition allows you to make informed decisions about your health and track progress effectively.
Risks of Excess Subcutaneous Fat
While subcutaneous fat doesn’t carry the same immediate health risks as visceral fat, having too much can still negatively impact your well-being. Excessive subcutaneous fat has been associated with:
· Insulin Resistance: Elevated fat levels can interfere with the body’s ability to regulate blood sugar, increasing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
· Cardiovascular Disease: Chronic inflammation caused by excessive fat storage can contribute to heart disease.
· Mobility Issues: Carrying excess weight can strain joints and muscles, leading to reduced mobility and chronic pain.
Maintaining a healthy amount of subcutaneous fat is essential for overall health and quality of life.
Tips for Managing Subcutaneous Fat
If you’re looking to reduce excess subcutaneous fat, here are some practical tips:
· Adopt a Balanced Diet: Focus on whole, nutrient-dense foods such as vegetables, fruits, lean proteins, and whole grains. Reduce your intake of processed foods and sugary beverages.
· Stay Active: Regular physical activity, including both cardio and strength training, can help burn stored fat and prevent further accumulation.
· Monitor Your Health: Tools like body composition scales and professional consultations can help you track progress and stay motivated.
Final Thoughts
Subcutaneous fat is a natural and necessary part of the human body, providing energy storage and protection. However, excessive amounts can lead to health concerns, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy balance.
By adopting a balanced diet and regular exercise routine, you can manage subcutaneous fat effectively and improve your overall health. Modern tools for tracking body composition, such as ultrasonography or calipers, can serve as valuable aids in this journey. Remember, the key to success is consistency and patience.
Take charge of your health today, and embrace the steps necessary to maintain a balanced and healthy lifestyle!
 Hot News
Hot News2024-12-16
2024-11-21
2024-10-17
2024-09-06
2024-01-24
2024-01-10